
Table of Contents
Introduction:
Email routing is a critical component of managing email services effectively within cPanel. By configuring email routing, users can ensure that incoming emails are directed to the appropriate destination, whether it be a local mail server, a remote mail server, or a backup server. This feature offers flexibility and control over how emails are handled, optimizing delivery and ensuring reliability for domain owners. Understanding how to configure email routing empowers users to tailor their email setup according to their specific requirements and infrastructure.
What is Email routing in cPanel ?

Email routing in cPanel determines how incoming emails for a domain are managed. Users can specify whether emails should be handled locally on the server, routed to a backup or remote mail server, or stored and forwarded. This feature ensures efficient delivery and management of emails based on the user’s preferences and requirements. It allows for flexibility in configuring email services, whether hosting emails locally, remotely, or through third-party providers, ensuring reliable email communication for domain owners.
The Features of Email Routing

- Automatically Detect Configuration: This option instructs the server to automatically detect the best email-routing configuration based on the server’s setup and the domain’s MX (Mail Exchange) records. It is the default option and is suitable for most cases.
- Local Mail Exchanger (LX): This option instructs the server to route emails locally if the mail server for the domain is hosted on the same server. Incoming emails are delivered directly to the server’s mailboxes.
- Backup Mail Exchanger (BX): This option specifies that the server should act as a backup mail server for the domain. If the primary mail server becomes unavailable, the backup mail server temporarily stores incoming emails until the primary server is back online.
- Remote Mail Exchanger (RX): This option instructs the server to route emails to a remote mail server specified by the user. This is useful when the domain’s email services are hosted on a different server or with a third-party email service provider.
- Store and Forward: This option is similar to Remote Mail Exchanger (RX) but also stores a copy of incoming emails locally before forwarding them to the remote mail server. This ensures that a copy of each email is retained on the local server
By configuring email routing in cPanel, users can ensure that incoming emails are handled according to their preferences and requirements, whether they are hosted locally on the same server, remotely on a different server, or through a third-party email service provider.
The uses of email routing
Email routing in cPanel serves several important purposes:

- Optimal Email Delivery: By configuring email-routing, users ensure that incoming emails are delivered efficiently to the intended destination, whether hosted locally on the same server or routed to a remote mail server.
- Backup Mail Handling: The ability to set up backup mail exchangers ensures that emails are stored temporarily on the server if the primary mail server becomes unavailable, preventing email loss during server downtime.
- Flexibility for Email Hosting: Users can choose to host their email services locally on the cPanel server or route emails to a remote mail server or third-party email service provider, depending on their preferences, infrastructure, and requirements.
- Load Distribution: Email routing can help distribute email traffic across multiple mail servers, improving performance and scalability, especially for high-volume email environments.
- Redundancy and Disaster Recovery: Storing copies of incoming emails locally before forwarding them to remote mail servers provides redundancy and enhances disaster recovery capabilities in case of mail server failures or network outages.
- Integration with Third-Party Services: Email-routing allows integration with third-party email services such as Microsoft Exchange or Google Workspace, enabling users to leverage advanced email features while still managing their domain’s email through cPanel.
Overall, email routing in cPanel offers users flexibility, reliability, and control over their email delivery, ensuring optimal performance and continuity of email services for their domains.
Steps to configure the email routing in cPanel
Log in to cPanel: Enter your cPanel username and password to access your account.
Locate “Email Routing”: In the cPanel dashboard, navigate to the “Email” section. Depending on your cPanel theme or layout, you may find it under different names such as “Email Routing,” “MX Entry,” or “Email Configuration.”
Access “Email Routing”: Click on the “Email Routing” option to enter the email-routing configuration interface.
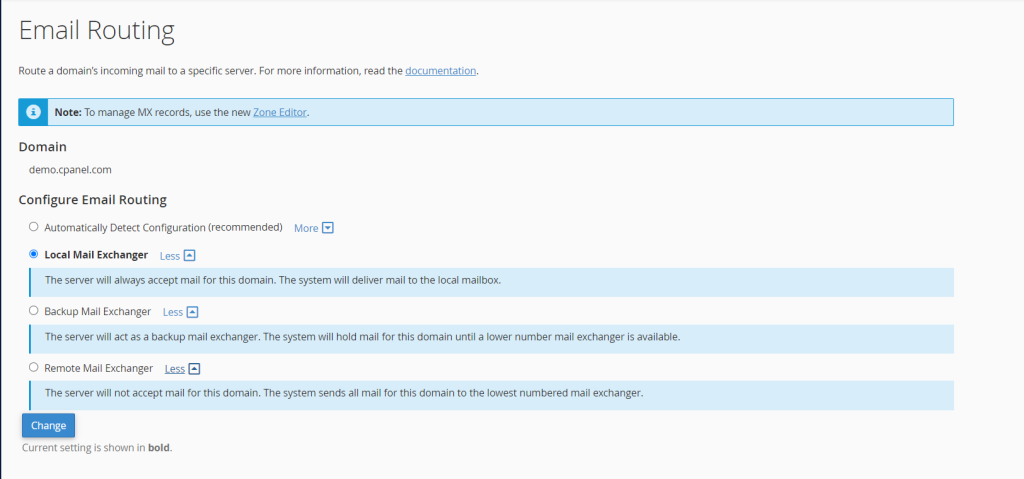
Select Routing Option: You will see various routing options such as “Automatic Detection,” “Local Mail Exchanger (LX),” “Backup Mail Exchanger (BX),” “Remote Mail Exchanger (RX),” and “Store and Forward.” Choose the option that best suits your requirements.
Apply Changes: After selecting the desired routing option, click on the “Change” or “Save” button to apply the changes.
Verify Configuration: Once the changes are saved, it’s a good practice to verify that the email-routing configuration is correctly set up. You can do this by sending a test email to one of your email addresses and checking if it is delivered as expected.
That’s it! You have successfully configured email-routing in cPanel. Remember that changes to email routing settings may take some time to propagate across the internet, so allow some time for the changes to take effect globally.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, email-routing plays a pivotal role in managing email services within cPanel. By configuring email-routing settings, users can determine how incoming emails are routed and delivered, whether it’s hosting emails locally, routing them to a remote mail server, or setting up backup mail handling. This feature provides flexibility, reliability, and control over email delivery, ensuring optimal performance and continuity of email services for domain owners. Understanding and properly configuring email routing is essential for maintaining efficient and reliable communication channels via email.
